Transcoding: "Transformation of the representation of information according to a certain code into another representation according to a different code." Larousse French Dictionary
The notion of intelligence at the urban scale is a phenomenon that has emerged in recent years. Several territories around the world are choosing to integrate technological processes to optimize their operations, create a sustainable structure, and improve the living conditions of their citizens. The organization of these smart cities and territories is based on the Industry 4.0 model which allows for flexibility, immediacy and a functionalist approach to technology.
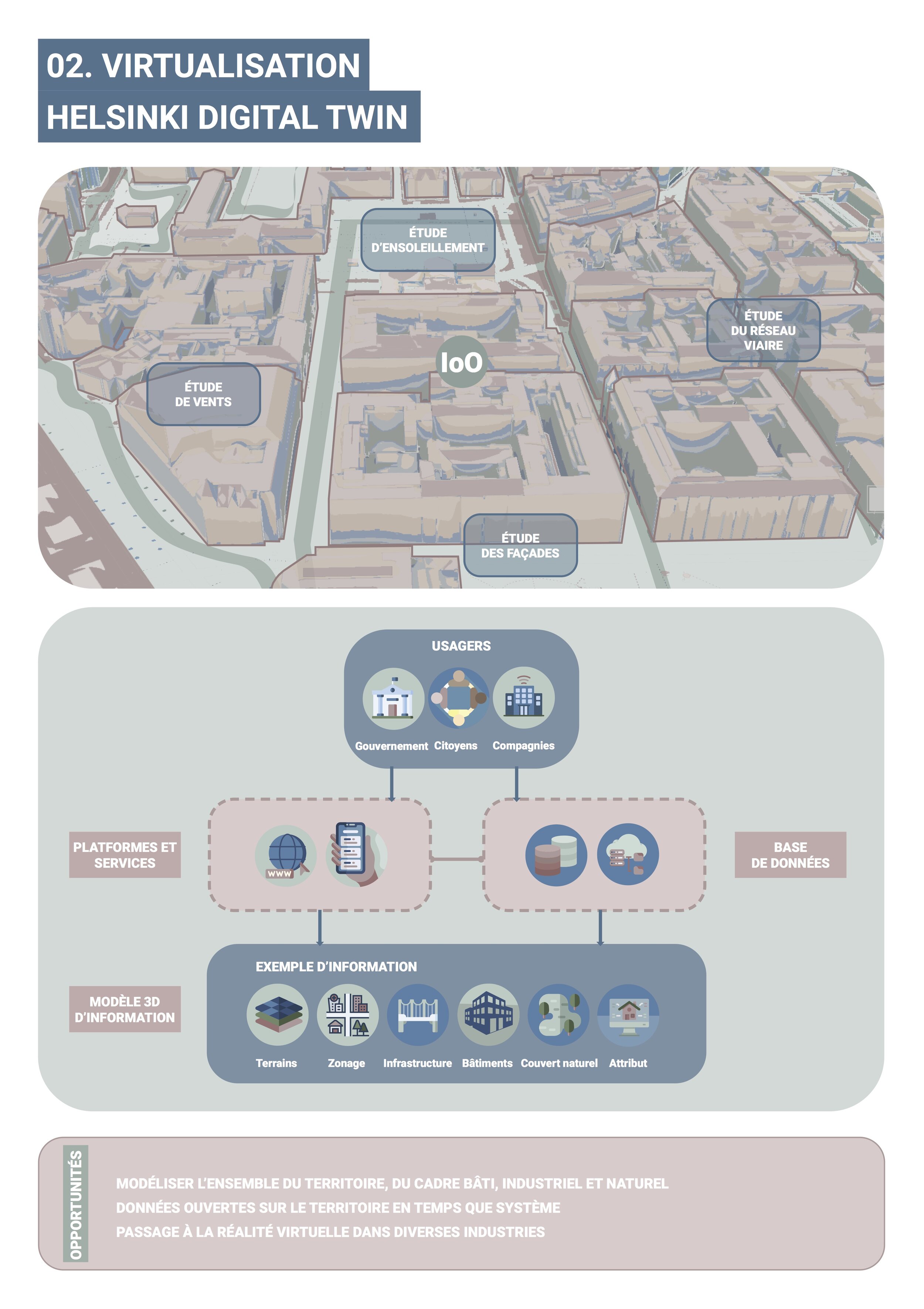
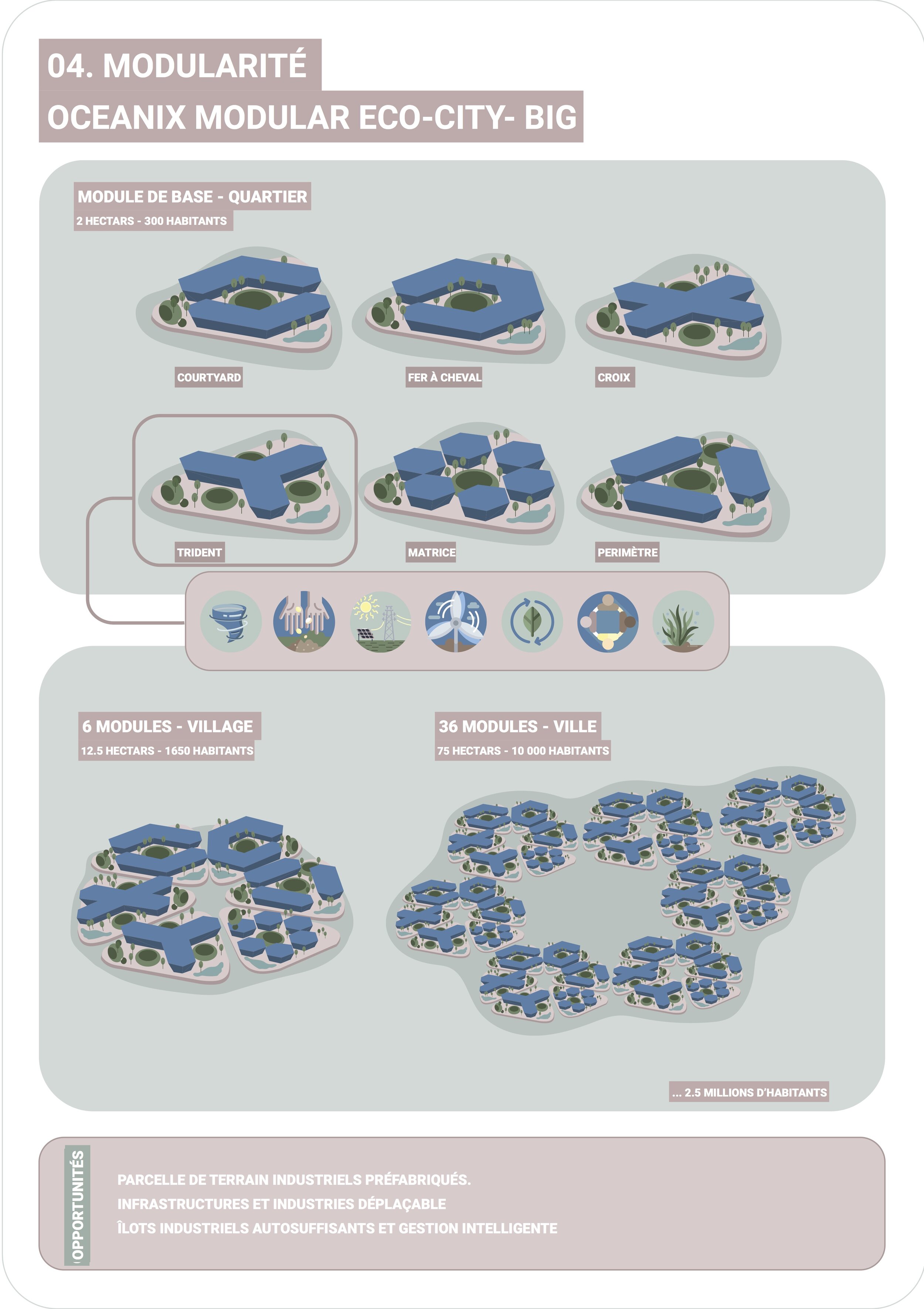
The entire fourth industrial phase is based on a process of production via the Internet of Things (IoO) which puts the product life cycle at the forefront. Thus, the term Industry 4.0 can be defined as a value chain organization whose technological components form Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS). These are defined as a retroactive network of computer elements that interact with each other. Their algorithms consider spatial, temporal and behavioral scales. The entire Industry 4.0 is based on six design principles: interoperability, virtualization, decentralization, modularity, real-time capacity, and service orientation.
The interconnection of these principles, applied in an urban ecosystem, would optimize the well-functioning of cities by adapting the logistics of the design process. The integration of technological processes in resource regions could promote the symbiotic cohabitation between industries and host cities. Research done in many smart cities and territories around the world has made it possible to draw out some concrete strategies for optimizing the geopolitical structure of the territories, which will eventually be applicable in Abitibi-Témiscamingue. Collaboration and a network that standardizes the various industries will contribute to the viability of these resource regions. This will be possible by integrating the different types of Internet (Internet of Things (IoO), Internet of Services (IoS), Internet of Energy (IoE), Internet of People (IoP) )) which will optimize the logistics of transport, energy use and services. The integration of cyber-physical technologies will also facilitate the connection between the environment and people, between the real world and the cybernetic world and between reality and virtual realities. The diversity of industries that share the same cyber-physical network will allow the city's economy to branch out, making it less dependent and more sustainable. The various issues of Abitibi-Témiscamingue that result from the fragmentation of the territorial system, will be transformed by projects that encompass the entire region, not by projects adapted only to industries. Will resource regions finally experience sustainability?